Curriculum
In ITB, students complete the bachelor program after taking the minimum of 144 credit unit (Satuan Kredit Semester / SKS) or 240 ECTS, offered in 8 regular semesters. Generally, all programs are conducted in two stages as follows:
- The Common Preparatory Level (Tahap Persiapan Bersama, TPB) is administered by the Institution for Common Preparatory Level (Lembaga Tahap Persiapan Bersama / LTPB). This stage initiates undergraduate study by strengthening the comprehension of basic sciences and enhancing required learning aptitudes. The normal duration of this stage is two semesters and consists of 36 credit units or 60ECTS. The student will first enroll in the
Faculty of Earth Science and Technology, and in semester 2, they will be
assigned to a study program based on their choice and first-semester
grade. Earth science introduction and basic geology in semester 2. - The bachelor’s stage (Sarjana) is administered by the study programs within each faculty or school. This is the stage for developing the knowledge and skills of the chosen discipline. The normal duration is 6 semesters with a minimum of 108 credit unit/ 180.36 ECTS. Students are given 6 years to complete the undergraduate stage, including the common preliminary stage.
Students may choose a program scheme during their study in the Geological Engineering program. Program schemes are alternatives for learners to complete their study level or continue their study to the next level. The preparation of schemes in the study program is intended to provide convenience and opportunities for learners to study disciplines in depth or breadth, according to their respective interests and abilities, to obtain competencies according to the needs of the world of work or the continuation of their studies, in an efficient time and process. There are five options that students can choose;
- Minor scheme: Students can take courses from any other study program listed as a minor course. Every study program sets core courses as a minor requirement. The minor scheme will be stated in the academic transcript
- Double major; student take all compulsory courses from other study program. The major will be stated in the academic transcript
- Bachelor-master integration/fast-track: Students take 12-18 CU of master courses in semester 7 or 8 in undergraduate.
- Specialisation: student takes elective courses based on the specialization package in their study program.
- Regular students take elective courses from any programs in ITB.
The curriculum structure of the Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering can be expressed in the form of a roadmap as in Figure 1.
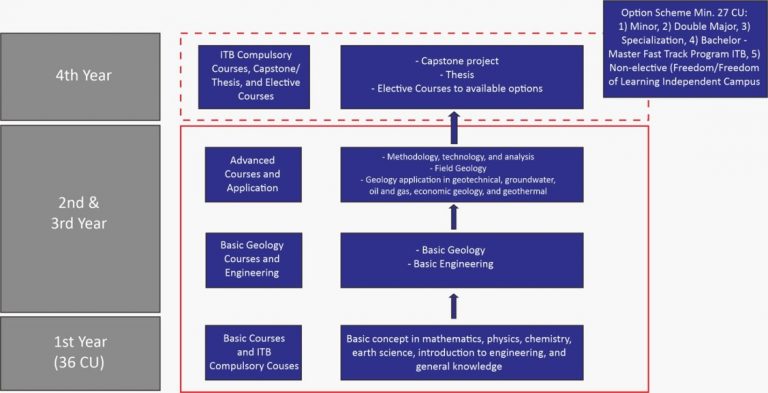
Figure 1. Road map of Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering
Undergraduate Program of Geological Engineering 2024 curriculum is divided into two stages, which is:
- First Year Preparation Program : 2 semester, 36 CU
- Undergraduate Program: 6 semester, 108 CU
According to the type, there are two type of courses in Geology, which is:
- Compulsory: 117CU
- Elective: 27 CU
Total Courses: 8 semester, 144 CU
| Programme | Stage | Total CU Pass | Minimum GPA | Maximum allowed duration of Study | ||
| Compulsory | Elective | Total | ||||
| Under-graduate | Common Preparatory | 36 | 0 | 36 | 2.0* | 6 years |
| Undergraduate | 81 | 27 | 108 | 2.0** | ||
* Minimum grade D; ** Minimum grade C.
Graduation rules is following the graduation rules in ITB with addition of:
Undergraduate program can be done with total CU passed of 144 CU and has enrolled and passed the colloquium, comprehensive test, and final project defense as final step of students Final Project.
Geological Engineers should be able to deal with future challenges, such as issues related to non-renewable energy (fossil energy) and renewable energy, natural hazards and disasters, environmental (including groundwater issues), and development of earth sciences. The curriculum of Geological Engineering program is designed based on program learning outcomes so that graduates will be able to identify geological-related problems as well as providing engineering solution. Our graduates must be able to conduct standard data collection, processing and analysis, make geological interpretation, and identify engineering problems and then provide engineering solutions. Therefore they need a strong engineering and geological knowledge as their foundation. Basic sciences such as general chemistry, elementary physics, and mathematics become an integral part for comprehending various geological features and processes, and providing engineering solutions.
| Semester I | Semester II | ||||||
| Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | ||
| 1 | MA1101 | Mathematics I | 4/6.67 | 1 | WI2001 | Introduction to Engineering and Design | 3/5 |
| 2 | FI1101 | Elementary Physics I | 3/5 | 2 | WI2002 | Artificial Intelligence and Data Literacy | 2/3.33 |
| 3 | KI1101 | General Chemistry I | 3/5 | 3 | WI2005 | Indonesian Language | 3/3.33 |
| 4 | WI1101 | Pancasila | 2/3.33 | 4 | WI2004 | English | 2/3.33 |
| 5 | WI1102 | Computational Thinking | 2/3.33 | 5 | GL1201 | Physical Geology | 3/5 |
| 6 | WI1103 | Introduction to Principles of Sustainability | 2/3.33 | 6 | GL1202 | Crystallography and Mineralogy | 3/5 |
| 7 | WI1111 | Basic Physics Laboratory | 1/1.67 | 7 | WF1211 | Earth System | 3/5 |
| 8 | WI1112 | Basic Chemistry Laboratory | 1/1.67 | ||||
| Total | 18/30 | Total | 18/30 | ||||
| Semester III | Semester IV | |||||||
| Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | |||
| 1 | WI2003 | Sports | 2/3.33 | 1 | WI201X | Religion | 2/3.33 | |
| 2 | GL2101 | Mathematics and Statistics for Geology | 2/3.33 | 2 | WI2006 | Civic Education | 2/3.33 | |
| 3 | GL2102 | Geofluid | 2/3.33 | 3 | GL2201 | General Geochemistry | 2/3.33 | |
| 4 | GL2103 | Rock and Soil Mechanics | 2/3.33 | 4 | GL2202 | General Geophysics | 2/3.33 | |
| 5 | GL2104 | Structural Geology | 3(1)*/ 5(1.67) | 5 | GL2203 | Stratigraphy | 2/3.33 | |
| 6 | GL2105 | Paleontology | 2/3.33 | 6 | GL2204 | Geomorphology | 2/3.33 | |
| 7 | GL2106 | Petrology | 3(1)*/ 5(1.67) | 7 | GL2205 | Tectonophysics | 3/5 | |
| 8 | GL2107 | Sedimentology | 3(1)*/ 5(1.67) | 8 | GL2206 | Optical Mineralogy and Petrography | 3(1)/5(1.67) | |
| 9 | GL2207 | Micropaleontology | 3(1)/5(1.67) | |||||
| Total | 19/31.67 | Total | 20/33.33 | |||||
| Semester V | Semester VI | |||||||
| Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | |||
| 1 | GL3101 | Information System and Remote Sensing for Geology | 2/3.33 | 1 | GL3201 | Law and Regulation on Earth Management | 2/3.33 | |
| 2 | GL3102 | Historical Geology | 2/3.33 | 2 | GL3202 | Geology of Indonesia | 2/3.33 | |
| 3 | GL3103 | Reference Study | 2/3.33 | 3 | GL3203 | Methods for Field Geology | 2/3.33 | |
| 4 | GL3104 | Geological Hazards and Environmental | 2/3.33 | 4 | GL3204 | Field Geology Mapping | 3/5 | |
| 5 | GL3105 | Volcanology | 3/5 | 5 | GL3205 | Petroleum Geology | 3/5 | |
| 6 | GL3106 | Engineering Geology | 3(1)*/ 5(1.67) | 6 | GL3206 | Hydrogeology | 3/5 | |
| 7 | GL3107 | Mineral Deposit | 3(1)*/ 5(1.67) | 7 | GL2207 | Geothermal Geology | 2/3.33 | |
| 8 | Elective Course | 2/ 3.33 | 8 | WI2023 | Business Management and Entrepreneurship | 2/3.33 | ||
| Total | 19/31.67 | Total | 19/31.67 | |||||
*(1) indicate lab/studio works credit unit
| Semester VII | Semester VIII | ||||||
| Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | Code | Courses Name | CU/ECTS | ||
| 1 | GL4049 | Design Project (capstone) | 3/5 | 1 | GL4050 | Final Project | 3/5 |
| Elective Course | 15/25 | Elective Course | 10/16.7 | ||||
| Total | 18/30 | Total | 13/21.67 | ||||
In semesters 7 and 8, elective applied courses are given to improve the ability to examine various problems in geology and other related sciences. At this stage, students should select elective courses according to their specific interests. By the end of this stage, students will take a final project to apply all their skills and abilities to synthesize geological problems. Geological Engineering Study Program offers six study specialisation for students (i.e., engineering geology, hydrogeology, petroleum geology, economic geology, geothermal, geoscience/general) that can be subdivided as follows
| No. | Code | Course | CU/ECTS | Spesialisation Scheme | |||||
| Enggineering geology | Hydrogeology | Petroleum geology | Economic geology | Geothermal | Geoscience | ||||
| 1 | GL4001 | Investigation of Geotechnics and Hydrogeology | 3/5 | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| 2 | GL4002 | Methods on Geological Exploration | 3/5 | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |||
| 3 | GL4003 | Rock and Soil Engineering | 3/5 | ✓ | |||||
| 4 | GL4004 | Geology for Underground Construction | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 5 | GL4005 | Geology in Infrastructure Engineering | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 6 | GL4006 | Geology of Construction Material | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 7 | GL4007 | Groundwater Modelling | 3/5 | ✓ | |||||
| 8 | GL4008 | Groundwater Drilling Engineering | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 9 | GL4009 | Geopressure | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 10 | GL4010 | Forensic Hydrogeology | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 11 | GL4011 | Well Log Analysis | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 12 | GL4012 | Unconventional Hydrocarbon Geology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 13 | GL4013 | Petroleum Geochemistry | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 14 | GL4014 | Reflected Seismic Interpretation | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 15 | GL4015 | Static Reservoir Modelling | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 16 | GL4016 | Sequence Stratigraphy | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 17 | GL4017 | Geological Computation | 3/5 | ||||||
| 18 | GL4018 | Mining Geology | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 19 | GL4019 | Hydrothermal Mineral Deposits | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 20 | GL4020 | Mineral Deposits and Ore Mineral | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 21 | GL4021 | Exploration and Enviromental Geochemistry | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 22 | GL4022 | Petrogenesis | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 23 | GL4023 | Geothermal Bore-hole | 3/5 | ✓ | |||||
| 24 | GL4024 | Rock Alteration | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 25 | GL4025 | Mapping of Thermal Manifestation | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 26 | GL4026 | Geothermics | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 27 | GL4027 | Instrumentation of Geothermal Geoscience | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 28 | GL4028 | Geology of Bandung Basin | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 29 | GL4029 | Geotourism | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 30 | GL4030 | Enviromental Geology | 3/5 | ✓ | |||||
| 31 | GL4031 | Geostatistics | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 32 | GL4032 | Geoarcheology | 2 / 3.33 | ✓ | |||||
| 33 | GL4033 | Marine Geology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 34 | GL4034 | Micropaleontology and Biostratigraphy | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 35 | GL4035 | Analytical Stratigrahy | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 36 | GL4036 | Vertebrate Paleontology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 37 | GL4037 | Invertebrate Paleontology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 38 | GL4038 | Advanced Structural Geology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 39 | GL4039 | Structural Petrology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 40 | GL4040 | The Rock Forming Mineralogy | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 41 | GL4041 | Urban Geology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 42 | GL4042 | Coal Geology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 43 | GL4043 | Selective Topics in Geology A | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 44 | GL4044 | Selective Topics in Geology B | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 45 | GL4045 | Job Training | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 46 | GL4046 | Digital Geology | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 47 | GL4047 | Geology of Carbon Sequestration | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
| 48 | GL4048 | Coal Characterization | 2 / 3.33 | ||||||
