DEGREE PROGRAM – STRUCTURE, METHOD, AND IMPLEMENTATION
Structure and Modules
The study program curriculum in ITB is arranged according to the institution vision and mission so that the graduates have high competence that correspondence with society needs and the development of the science, technology, and art.
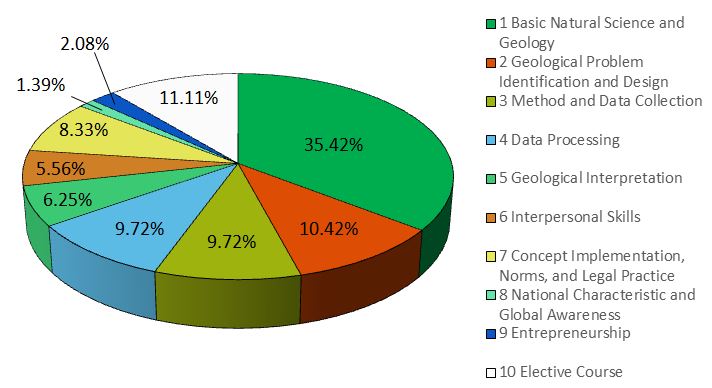
Relationships between subjects in the curriculum structure of the Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering are expressed in the form of a roadmap

Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering Study Roadmap
It is shown on the roadmap that the basic-subject courses is given in semester 1 and 2 (Common Preparatory Level). The subjects of mathematics, chemistry, physics, integrated science and language are needed to provide basic knowledge and logical perspective for the students to learn the concept of geology.
Knowledge in geological concept and methods in geological science is given in Semester 3 to 6 and refined with Field Geology course which is held by the end of Semester 6. In this stage, students will be equipped with the ability to collect the geological data, and analyze them to interpret the geological conditions. Field geology course will also provide opportunity for students to work both individually and as a team. In this stage, Reference Study course is also given in order to escalate student ability in communicating their ideas, both oral and written.
In semester 7 and 8, applied courses are given to improve the ability to examine various problems in geology and other related sciences. At this stage, students should select elective courses according to their specific interest.
By the end of this stage, students will take a final project in order to apply all of their skills and abilities to synthesize geological problems.
Course Learning Outcome
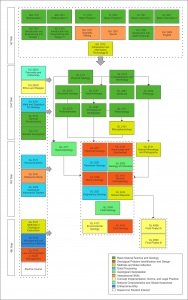
Course Learning Outcome is clustered according to the PLO that has developed by Undergraduate Program Geological Engineering with certain considerations. 48 compulsory courses with 126 credit units is grouped according to the PLO resulting the Undergraduate Program Geological Engineering course teaching weight diagram. Workload is designed taking into account the PLO pursued, methods and strategies of teaching, and also the availability of learning facilities. Courses in Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering are designed so that graduates are able to have all competencies based on PLO. Students are also able to develop his curiosity of specialized in some field by taking elective courses. In the curriculum of Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering, there are rooms to take at least 17 credits of elective courses (if students take the Final Project A), or 19 credits of elective courses (if student take Final Project B)
Course are clustered in 10 groups and the total workload for each cluster is given in table and displayed as pie-chart below
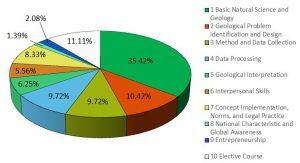
Work Load and Credits
Education programs in ITB refer to semester system. One academic year consisting of two regular semester, the first semester and the second semester, each of which consist of academic activities for 16 weeks. This 16 weeks of the course includes lecture time for a minimum of fourteen weeks and exams for two weeks. There is also one optional short semester. The first regular semester starts on August and ends on December, followed by the second semester on January until May. The short semester is offered from June through July for the students that are willing to improve their marks or shorten their length of study.
One credit hour in ITB for Undergraduate Program is equivalent to the student’s effort of 3 (three) hours a week in one regular semester, which includes:
1. One hour of scheduled academic activities with faculty, in the form of face-to-face activities in the classroom,
2. One hour of structured activities undertaken in the course of lecture activities, such as completing tasks, creating papers, tutorial activity, etc.
3. One hour of independent activity, which is an independent activity of student to explore and prepare academic tasks, such as reading reference books.
Undergraduate Program in ITB has minimum workload of 144 credit units which correspond to 5760 hours, or about 200 ECTS. Generally the credit units is distributed into 8 regular semesters . On average, total hour per year is 1440 hours. The normal workload for each regular semester is limited to 800 hours, corresponds to 20 credit unit (27.8 ECTS). Normal workload for each short semester is limited to 400 hours, corresponds to 10 credit unit (13.9 ECTS). Thus, normal workload per week for each regular or short semester is around 40 hours.
However, ITB encourages its students with outstanding achievements to systematically accelerate their study with this below requisites:
1. Students with outstanding achievements can propose their acceleration of study with the approval of their academic advisor and the Head of the Program. Students with this approvals can take workload more than the normal limit allowed for each semester.
2. Regulations of maximum workloads allowed for undergraduate program students with outstanding achievements are as follows:
a) Students having average score of ≥ 2.75 (of maximum score of 4.00) in the previous semester can take the workload of maximum 22 credits in a regular semester.
b) Students having the average score ≥ 3.75 (of maximum score of 4.00) can take workload of maximum 24 credits in a regular semester.
As mentioned before, according to ITB Rule, one credit unit (CU) for Undergraduate Program has an academic load equivalent to 3 (three) hours* a week of the student’s efforts within one regular semester which comprise:1. 1 (one) hour of scheduled contact with the teaching staff in learning activities.
2. 1 (one) hours of structured activities related to lectures, such as doing assignments, writing papers, or literature study.
3. At least 1 (one) hour of independent activity to obtain better understanding of the subject matters and to prepare academic assignments such as reading references.
(*) Note that one hour in our curriculum is equal to 50 minutes work.
Table 2 2 Normal credit units and the corresponding workload per semester.
Academic Year Semester Common Preparatory Level Bachelor stage Total Hours ECTS (28.8 hours per credit)
For course with practical work, lab work, final project courses, fieldwork courses, and another similar activities, one credit unit is equal to 3 (three) to 5 (five) hours a week of students activities. For courses with lab work, workload for lab work is embedded in the credit unit of that particular course. No particular credit unit is given lab work part. Workload due to the lab work is counted in the course evaluation to determine student grade.
In principle, ITB recognize of the course taken by student at Partner University to the same award title, however, it must have the same credit unit value, structure, and requirements, and ITB has MoU with respective university. Transfer of credits is only possible if an agreement exists between the involved universities which regulate the details of the transfer, such as the list of courses that can be transferred, the minimum grade, equivalency of curriculum between universities, etc.
Course planning
Student must enroll and complete all compulsory and their elective course within the curriculum sequentially in accordance with the provisions of the curriculum. In planning their courses, students are required to take all the compulsory subjects and some elective courses. Students are permitted to take the number of course more than the number of the entire required courses. Students are required to take courses according to their order in the curriculum, i.e., by taking the lower level-and-year courses first.
At the end of each semester, students who take a number of CU of workloads will be granted CU according to the CU courses that pass the evaluation/examination. Compulsory courses that do not pass the examination need to be re-taken at other semester and the CU do not counted as work load. If students have passed evaluation/examination, they are expected to achieve the respective learning outcome set by that particular course.
Teaching Methodology
The teaching and learning activities in the Undergraduate Program Geology Engineering are conducted both indoors and outdoors. Class room activity is conducted with the student capacity ranging from 5-90 students. Laboratory facilities are available to support the education processes. The process is designed to be open so that students are free to interact with lecturers in various issues, such as study planning, lectures, final project, as well as the student extracurricular activities. Students are encouraged to ask and discuss to trigger their critical thinking. Field activities are important because student can observe and measure directly the geological object, and produce geological map.
Teaching & learning methods implemented in Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering.
Teaching & Learning methods Description Contact hours Independent work
Lecture Lecture is the primary method to deliver various courses which give students knowledge and understanding of all course topics. The class size varies according to the course subject, normally between 40-80 students for compulsory courses, and 5-25 students for elective courses. Minimum participant of 5 students is applied to run any course. Conventional teaching normally uses board and LCD projector, however, in some courses ICT based-lecture is used 2 hour per week per CU At least 1 hour per week per CU
Tutorial At most lectures, tutorial is given as complimentary lecture to enhance understanding of concept of topics discussed. The size of tutorial class in most courses similar to that of the regular lecture class Average 1 hours per week
Laboratory class Some lectures give a laboratory class and practical as complimentary to enhance the understanding of geological concept, analysis, and methods. The size of practicum class in most courses is depends on lab facilities and normally 20-30 students. Average 1 hours per week At least 2 hours to prepare the lab report
Independent study Independent study is the course which students doing some literature studies on the topic that he/she get interest. Upon doing that, an independent study advisor is assigned for the student to provide advice in order that the goal of the study is attained. The topic studied is varied, however, most of the topics are within the expertise of the faculty staffs Contact with advisor at least 1 hour per week Average 5 hours per week
Final project Final project is a course that student studying and doing research in a particular field of interest. Final project is an effective mean for students to expose them in a research atmosphere. Final project is offered in two semesters and students can start the project either in semester I or semester II Minimum of 8 times progress report with advisor(s) 3 – 5 hours per week per CU
Research based learning class To get more experience and deep understanding of the topics, few classes are run with Research Based Learning (RBL) method. In this method students are expected to do research, either literature study or doing some simple research project, on the given topics of course. At the end of the course, usually students have to present their findings in the form of report and presentation At least 8 hours per semester At least 16 hours per semester
On Job Training This course is generally done in company. The focus of the study and location of the company are chosen by the student themselves. This activity is dominated with independent study and learning process which is taught by the off-campus institution (generally is held by student’s advisor from a company). Discussion and presentation in front of lecturer and/or student’s advisor is done in the course. Tentative, following the company’s work hour. Minimum 80 hours or 2 weeks At least 160 hours or 4 weeks
Excursion / Site Visit Site visit in general is held in site which has unique geological condition or geological outcrops which are related to certain study course. This activity is held in at least once at the end of semester (especially for geological course) At least 10 hours per activity At least 24 hours to complete an activity report
Field work This course usually takes place in Karangsambung-Kebumen, Central Java. The main activity is that the students practice to do a geological mapping. This activity is done by executing several geological methods e.g. outcrops observation, pace-compass mapping methods, stratigraphic measuring section, structural geology analysis, geological sketching, observation, and interpretation.
The geological activities is executed with a guidance by lecturers and field assistants for the data collecting, data processing and final report’s making, including maps making. At least 30 days (4 hours per day) At least 6 hours per day to prepare the field work for next day and to perform the data processing
Support and Assistance
ITB provides supportive learning environment that covers the entire span of studies to ensure students finish their study timely and accordingly. The environment effectively supports students’ studies and learning. The environment also facilitates students to complete their studies by following an appropriate study plan that they have prepared themselves and to graduate within the desired time.
The following is a partial list of personnel and units and its role and duty as part of academic support provided by ITB.
Academic Advisor (Wali Akademik)
As students commence their study at the common preparatory program/Tahap Persiapan Bersama (TPB), academic advisors are appointed for them. The academic advisor plays the role as a “parent-like” who give advice to students for their success to complete the TPB program. One academic advisor will be responsible to supervise about 20 students. Usually academic advisor welcomes for every consultation that may students need, even for any problems beyond academic matters. Student academic data (study progress and performance) are monitored and well-recorded at the university level through academic information system. Academic advisor can access all the data of the students at any time. Based on the students’ performance, academic advisor give consideration on what courses should be taken by student for each semester through students online account in http://ol.akademik.itb.ac.id. In the case of students have problems related to the academic program, academic advisor is then well informed and gives any advice to the students since the system provide student monitoring mechanism and early warning.
For the second year students, the academic advisor from the same study program is appointed for them. The role and the responsibility of the academic advisor is the same as that of the first year program. Advisor regularly meet with students before the beginning of each semester to determine courses that each students should register for the coming semester. This course selection is based on the course eligibility as determined by the prerequisite structure of the curriculum, and other considerations such as the students’ personal preference (in the case of elective courses), their extracurricular activities, etc. All students are required to obtain advisor approval for selection of courses during pre- registration before they can register on-line for the courses. The advisors also address any issues directly or indirectly related to the students learning process as well as personal issues that may impact students’ learning capability.
Each student has semi-annual study plan that is recorded electronically at the university level and that indicates the courses have been approved. Academic Advisors can also access the student records which consist of, among others, courses taken in the current or previous semester along with the student’s performances. The academic advisor will be handed over to the final project supervisor as students take the final project. All academic problems that come up during final project works should be discussed with supervisors.
Academic Advisors are also involved in career counselling, selection of Research Division, application for grants and scholarships, coaching for student extracurricular activities, and other program support activities.
Procedures on academic advisory system is available at http://ol.akademik.itb.ac.id.
Counselling Centre
Students can consult their academic or non-academic problems in Counselling Centre. Counsellor teams are instructor staff of ITB and have certificate as counsellor from National Training for Student Counselling Officer (Penataran Nasional Petugas Bimbingan dan Konseling).
Students Affair Office
ITB provides scholarship for students who eligible for that. All type of scholarships are managed and organized by Students Affair Office/Lembaga Kemahasiswaan (LK). LK manages application, selection and distribution of scholarship. Study program provides recommendation and approval to eligible students. Various types of scholarships are offered to students, such as: economy scholarship, achievement scholarship and supreme scholarship. The scholarship comes from various sources, such as: ITB Parents Union (IOM), Alumni, Local Government, Multinational Company, State Company, and Indonesian Ministry of Education.
Soft Skill Improvement
• Seven habits of highly effective students
• Success strategy training for students
• Student chapters
• Entrepreneurship training
• Thematic Field Work
Non-Academic Support Units
Central Library
The central library provides information services to ITB and society. It has about 225,000 book titles, journals, e-books and e-journals. The services include lending books, audio visual, ordering copy from other libraries in Indonesia and overseas, and internet services. Central Library’s members are lecturers, students, administration staffs and alumni.
ITB Publisher
ITB have a book publisher that helps lecturer to publish their book. Many of lecture notes are published through ITB Publisher and can be sold less expensive.
Computer Laboratories
Comlabs provide services for academic civity such as courses, public access (internet, typing, AI3, students email, print, backup data, download, and etc.), information technology service (Microsoft Legal Software, AI3 account, hotspot, web hosting, IT consultation), special service (workshop and IT seminar, Free Saturday Lesson, Bulletin IT).
ITB Network Account
ITB provides students with an ITB Network Account (INA) which can be used to access every information and technology service in ITB. ITB Network Account is account which is used by academic civity of ITB to access various information and communication technology services in ITB. INA is one of logins which is used for all services, such as email account, FTP, My ITB portal, hotspot, VPN-ITB, digital telephone, and ITB Digital Library Access (Digilib).
E-Learning
This system is developed to support the academic activities in ITB. The collaboration between lecturers and students is expected to be more intensive. Students can access this system after registration. E-Learning of ITB (http://kuliah.itb.ac.id) has an appearance which makes the users feel comfort to follow the courses. Besides that, it can also motivate the owners of the contents to add the courses materials so that this E-Learning becomes more complete.
Hotspot ITB
ITB Hotspot is wireless connection service, located in strategic places around ITB. To use this service, users must have sets of computer equipment, laptop or PDA, which has wireless LAN (Wi-Fi) 802.11b/g. User is asked to enter username and the password of ITB Network Account (INA) as authentication system, and set proxy HTTP on the user browser to: cache.itb.ac.id with port 8080.
For more information about ITB Network Account (INA) or to get ITB-INA, user can call Unit Sumber Daya Informasi ITB (USDI- ITB) office. ITB-INA service also provides voucher for every day wireless connection.
Career Centre
At the Institute level, career development is undertaken by the ITB Career Development Centre (ITB CDC). ITB CDC maintains an on-line job application and career opportunity information system that all ITB students may access after registering as CDC members. A considerable number of fresh graduates have utilized services provided by ITB CDC. Career Centre encompasses a broad range of Programs designed to assist undergraduates, graduate students, and alumni of the University to explore their career options. The Career Centre acts as job supply (on this case, private or public industry) to maintain students’ professionalism both on specific field (by technical training) and generic field (soft skills training).
Language Centre
ITB Language Centre offers courses for ITB students and staff, as well as for groups outside of ITB. ITB language Centre specializes in Pre-departure courses, TOEFL Preparation Courses, and Courses in English for Specific Purposes especially in science and technology.
The Language Centre offers the following services:
a. English, Japanese, and German courses.
b. Translation
c. TOEFL-like Test
d. Language Consultant
e. Language Training for English Teachers
f. Indonesia Course for Expatriates
Health Service
Bumi Medika Ganesha is ITB’s health service for students and faculty members. The main purposes of the health service are the diagnosis, the treatment of illness, the activation and maintenance of well being and the promotion of health education Programs. Bumi Medika Ganesha Health Services are:
a. General Practitioner
b. Dentist
c. Specialist
d. Family Planning Practical
e. Rontgen and EKG
f. Healthy Statement Letter (Surat Keterangan Sehat)
g. Laboratory Clinic
h. Pharmacy (Apotek Bumi Medika Ganesha)
i. Health Consultation
j. Acupuncture
Sport Centre
The Sport Center has Olympic-size swimming pool, diving pool, football field, basketball fields, volleyball fields, tennis courts, jogging track and fitness center. The facilities are mostly used for sport courses in the Common First Year Program. The facilities are also used for other activities such as football school, tennis and swimming class programs, jogging club, and other programs.
Student Dormitories
ITB has several dormitories available for students (Table 2-4). But mostly the students rent their own housing or apartment near the university.
Student Chapter
ITB has many student chapter clustered into 6 clusters, Sport Units, Education Units, Discussion Unit, Religion Units, Art and Culture Units, and Media-Journalistic Units. Total of this unit is about 80 units and keep increasing every year. Beside of this units, ITB also has student chapter for their own department, in Undergraduate Program in Geological Engineering we have HMTG GEA ITB, the Geology Student Union. We also encourage students to join national or international student chapter available for geology students such as American Association of Petroleum Geologist (AAPG), Society of Economic Geologist (SEG), Student Chapter of Indonesian Geologist Society (SC-IAGI), etc.
Table 2 4 Dormitories available around ITB Ganesha
Dormitories Address Capacity
H Dormitory Jalan Cisitu Lama 27, Bandung 23
Kidang Pananjung Jalan Kidang Pananjung 300
Bumi Ganesha Jalan Cisitu Baru 35, Bandung 120
Kanayakan Jalan Kanayakan Lama 61, Bandung 180
Sangkuriang Rusunawa Sangkuriang group house 192
Evaluation of Structure, Method, and Implementation
Strength
1. Implementation of curriculum is supported by appropriate learning methods.
2. The teaching and learning methods implementation in study program is organized well.
3. There are so many support facilities that could be used for students to improve them both on academic and non-academic.
Weakness
1. The study program is difficult to synchronized the PLO 8 (Nationalism and Global Awareness) as well as PLO 9 (appreciation of entrepreneurship) into courses.
2. Lack of mechanism for the final project students to prepare their research and to map their topic of interest.
3. Internship program for the students is still not compulsory.
Area for Improvement
1. The study program will create some form of activities to fulfilled PLO 8 and 9.
2. The study program needs to create a firm mechanism for final project students to prepare their research and to map their topic of interest.
3. The study program need to consider internship as a compulsory course.